Septic Tanks & Septic System Components
- Understand the functions of septic tanks.
- Learn how septic tanks can be constructed and the important design features.
- Discover that aerobic bacteria consume far more organic solids in septic tanks than anaerobic bacteria do.
- Learn about the three key layers within septic tanks and what each contains.
- Discover that Aero-Stream can successfully execute a controlled aerobic conversion of your septic tank, saving your system and thousands of dollars compared to system replacement!

Septic Tank Overview
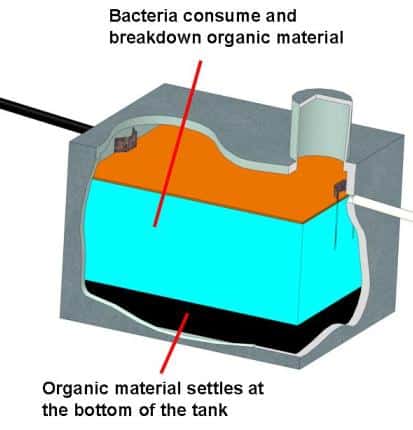
The major functions of a septic tank is:
- be a holding volume where a small percent of solids can be split from the liquids
- digest solids with a bacteria based biochemical process
- be a holding container for the settled solids prior to pumping the tank
In a passive anaerobic septic system, 40% of the solids are treated in the septic tank with the remaining 60% being treated in the drain field.
Note: In a septic tank retrofitted with an Aero-Stream® Remediator System, 90% of the solids are treated in the septic tank and only 10% are treated in the drainfield.
The Design of Septic Tanks
The most common material used to make septic tanks of are of plastic, fiberglass, steel or concrete. Septic tanks range in volume from 500 gallons for small septic systems to thousands of gallons for larger systems. These tanks are normally located underground. 1,000 to 1,500 gallons are the most typical septic tank sizes for a standard residential septic system.
The design of septic tanks can vary greatly. They can have multiple chambers or a single treatment chamber, dependent on the system requirements. Septic tanks one outlet in the final chamber and one inlet in the treatment chamber. The outlet pipe is at a lower height than the inlet. This allows the effluent to flow in one direction towards the outlet. Preferably the septic tank will have a septic tank risers installed. A plastic septic tank risers can be added to make maintaining the system easier if a riser was not installed originally.
Multi-chamber septic tanks are connected through a single opening. The 1st of a multi chamber of the septic tank is referred to as the trash chamber. This is where the influent is received and the majority of the biochemical process occurs.
The second chamber (if one exists) is referred to as the treatment chamber if it is an aerobic system. If it an anaerobic system the 2nd chamber is referred to as settling chambers. A cascading flow occurs in multi-chamber tanks. They are designed to act as a holding system which increases holding time. The effluent is more completely treated prior to flowing to the drain field.

What Happens Inside a Septic Tank
- the sludge zone
- the “clear” zone
- the scum zone.
The solids settle at the bottom of the septic tank because they are heavier than the water. These solids are named the sludge zone. Because there is a lack of oxygen at the of the septic tank bottom, anaerobic bacteria live in the sludge zone. The biodegradable solids are broken down and digested by the anaerobic bacteria. The solids become lighter as they are digested and move upward to the center clear zone of the tank.
Brown, murky water containing fine and microscopic biodegradable and non-biodegradable materials in suspension are found in the “clear” zone in an anaerobic septic tank. Anaerobic bacteria dominate this layer. This layer can contain some aerobic bacteria, however, they quickly die. As the water leaves the “clear” zone it moves to the drainfield. It will have anaerobic bacteria in the discharge. The bio-mat in the drainfield feeds off of the undigested organic material. This is the cause of drainfield failure.
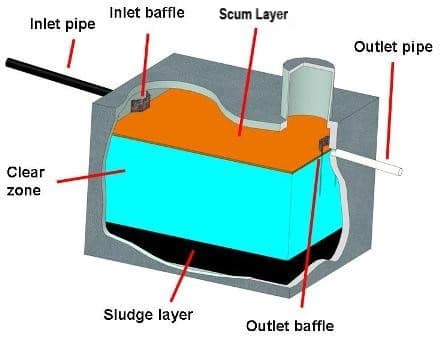
Greases, oils, soap films, and any other materials that are lighter than water and are located in the scum zone at the top of the septic tank. Both anaerobic and aerobic bacterium survive in the scum zone, but again, the anaerobic bacteria are dominant. The scum becomes heavier than water as it is digested. It sinks to the floor where it becomes sludge and is treated further.
The outlet baffle acts as a dam at the liquid surface level of the tank. It prevents the scum at the top of the septic tank from leaving the tank before treatment is complete. Solids of any size and weight must move into the “clear” zone as mentioned above to flow through the outlet baffle. This process occurs in each septic tank chamber.
Baffles in Septic Tanks
For additional treatment, an effluent filter is placed inside the outlet baffle. This can be a fine plastic mesh screen with slots or a bristle style filter similar to a large bristle brush. The filter stop solids that are larger than the open-area of the filter from flowing from the septic tank. If a bristle filter is installed that Aero-Stream offers, bacteria can grow on the filter bristles surface and further clean the effluent as it flows out of the tank to the drain field. If an effluent filter is located in the outlet baffle the addition of a septic tank riser is recommended so the filter can be serviced easily.
During high liquid levels there is an advantage of having an effluent filter. A significant amount of solids can flow out of the septic tank into the absorption field from the scum zone without a filter installed. This will not happen with a filter installed. The overflowing water will need to pass through the filter and be partially treated.
The trash chamber of the septic tank may or may not have an inlet baffle present. The inlet looks like the outlet baffle, but it is attached to the septic tank at the inlet hole of the tank. The inlet baffle terminates in the “clear” zone of the tank. The purpose of the inlet baffle is to prevent short circuiting of the wastewater during surging. The influent is always forced through the treatment process with the inlet baffle. Without the inlet baffle the wastewater could flow towards the outlet baffle and exit the tank without being treated. The inlet baffle also prevents solids from piling up on the scum zone and blocking the inlet pipe.
The Septic System Owners Manual
Nobody plans for the expense of having septic tank problems. Whether your septic system is new or failing, this manual is a must read for any homeowner.
Understand the causes and discover the solutions to your septic system and septic tank problems.
- The Reality of Your Septic System
- Terminology and Definitions
- Understanding Septic System Costs
- How Does a Septic System Work?
- Septic System Components – Septic Tank
- Septic System Components – Drainfields I
- Septic System Components – Drainfields II
- Septic Tank Problems – How a System Fails
- Resolving Septic System Problems
- Septic System Use and Maintenance Guidelines
